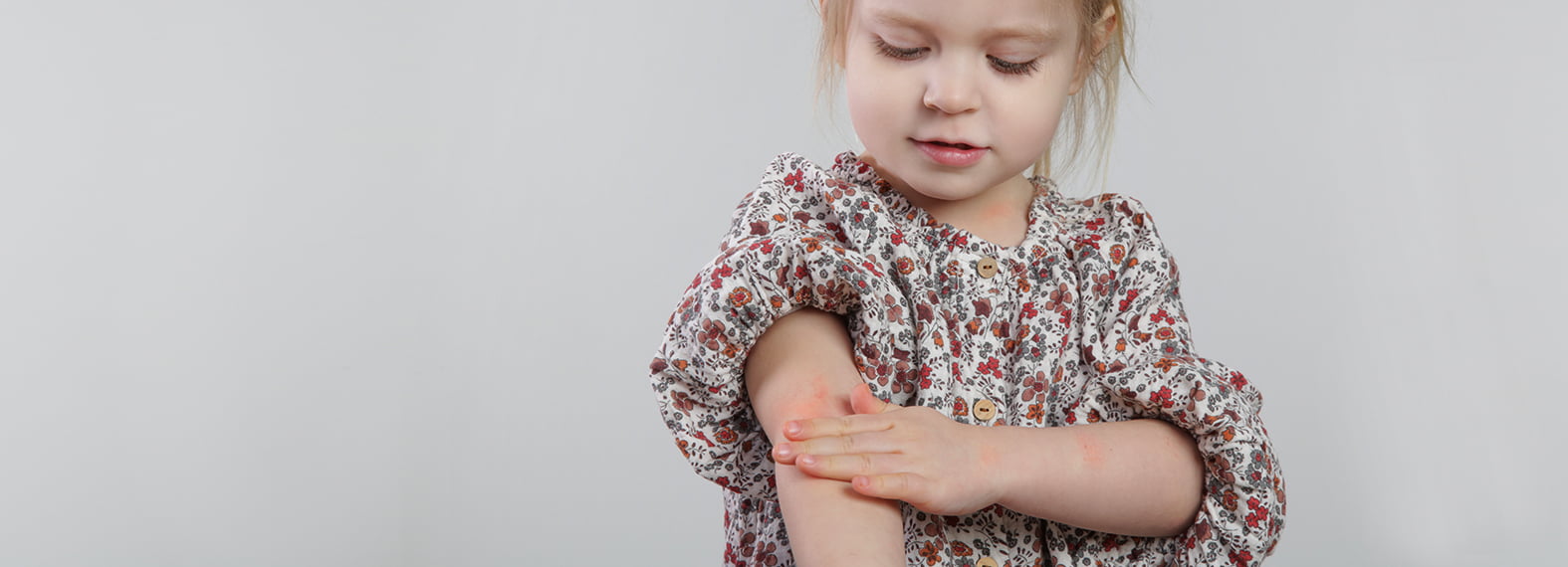
Urticaria is a reaction of our skin to allergens, irritating chemicals, plant toxins or physical stimuli. The symptoms include severe itching, a rash with pustules and a circumscribed reddening of the skin. In some cases, swelling of the skin and mucous membranes can occur, so-called angioedema. A common cause is an excessive release of histamine. In urticaria as a result of skin allergies, the body's own messenger substance is increasingly released. The triggers for urticaria are manifold - the most common cause is an allergic skin reaction. The rash is divided into acute and chronic urticaria.
Acute urticaria occurs in connection with an infection, among other things. This can be a viral infection, an acute food allergy or an intolerance to specific insect venoms (e.g. bee or wasp stings) or active ingredients of medicines.
The trigger of acute urticaria can usually be determined quickly and reliably, as the skin reaction usually occurs shortly after the irritation. For example, as a direct result of a wasp sting. Acute urticaria usually only lasts for a short time, for a few hours or days.
Chronic urticaria is a little more difficult to identify. This can also be triggered by allergies, but it usually occurs as a result of mechanical and physical stimuli such as scratching, tight clothing or very high temperatures. Severe physical and psychological stress can make the symptoms much worse. We speak of chronic urticaria when the symptoms persist for more than six weeks. Interruptions (symptom-free periods) are included.
For all types of hives, you should consult a specialised doctor (dermatologist). At the Swiss Derma Clinic in Zurich, we diagnose and treat all forms of skin allergies and urticaria. By reliably identifying the trigger, the recurrence of urticaria can be avoided in many cases.