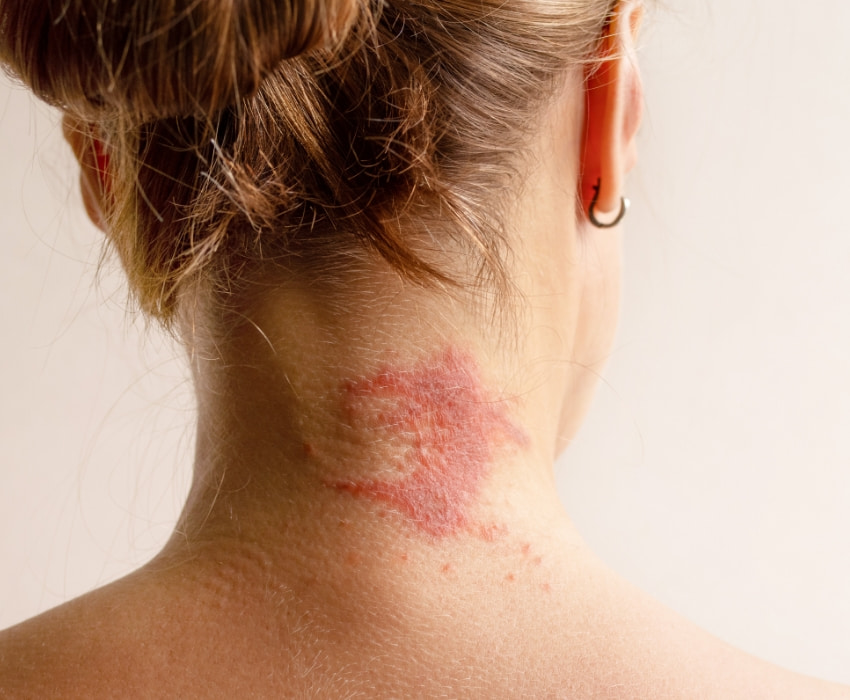
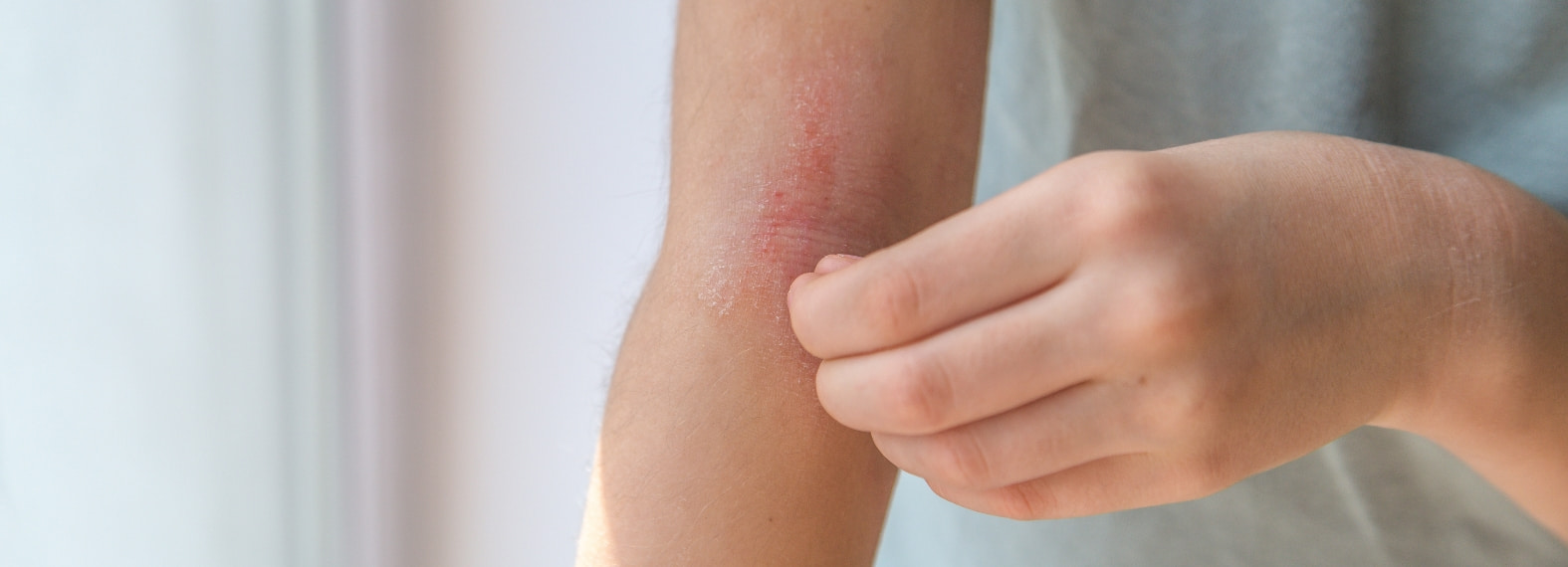
What is Eczema?
When eczema is diagnosed, it is important to note that it is not contagious! The affected skin area is red, and blisters and scales may form. It is often accompanied by mild to severe itching. Eczema (dermatitis) can manifest in different ways—there are various forms and triggers. For instance, contact dermatitis is a reaction to specific biological or chemical substances. In contrast, atopic eczema (or atopic dermatitis) is a chronic condition often associated with allergic diseases such as hay fever or asthma.
Soothing the Immune System in Atopic Dermatitis with Biologics
A very effective approach is treatment with biologics, such as monoclonal antibodies. These specifically target the body's own signaling molecules (interleukins) involved in the typical inflammatory reactions with itching and eczema. Because biologics act in a targeted manner, their side effects are generally significantly lower. Current studies confirm the impact of monoclonal antibodies on atopic dermatitis and their positive effects on quality of life.
Causes of Eczema
Many factors can cause dermatitis, including:
- Genetic predisposition to atopic conditions, particularly neurodermatitis or psoriasis.
- Environmental factors and allergens such as pollen, animal dander, or house dust mites.
- Irritating substances such as paints, chemicals, or fragrances.
- Skin irritation due to frequent hand washing, intense heat and cold, or disinfectants.
- Stress can also be a cause of dermatitis or exacerbate it, especially in chronic forms.
Symptoms of Eczema
We distinguish between acute and chronic eczema. The appearance can vary depending on the severity. Patients often come to us with the following complaints:
- Dry and sensitive skin
- Moderate to severe itching
- Discolored skin patches (brownish or reddish)
- Swelling (hives)
- Scaly and crusted areas
Important Note: All these symptoms may only occur temporarily and may improve briefly before worsening again. If this is the case for you, please call us or contact our clinic in Zurich.
Your Diagnosis at the Swiss Derma Clinic in Zurich
To make an accurate diagnosis, we will first conduct a thorough examination and inquire about your medical history as well as your family's. In some cases, a genetic predisposition may cause dermatitis. Sometimes, an allergy test can also be helpful to identify triggers such as pollen, grasses, or certain foods.
Your Treatment in Zurich
Many types of eczema can be effectively treated. The treatment aims to relieve symptoms, increase moisture, strengthen the skin barrier, and reduce inflammation.
Modern biologics also offer new therapeutic options for atopic dermatitis. Monoclonal antibodies are advanced medications that target the specific parts of the overactive immune system involved in inflammation. This approach differs from traditional medications like steroids, which broadly affect the immune response.
Additionally, appropriate creams can keep the skin supple and help prevent future flare-ups to some extent.
Traditional methods include:
- Topical steroids to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: Medications that relieve itching.
- Soothing and moisturizing ointments, serums, or creams.
- Light therapy with special UV light (depending on the type of eczema).